Describe the Atomic Orbital Shown in This Picture.
Okay So this was that which Adam has following Alberto Diver. Explain the variation of wavefunctions as the radius increases.

Electronic Orbitals Physical Chemistry Electron Configuration Teaching Chemistry
N3 l2 ml-2 b.

. C There will be more electrons ejected. In atomic theory and quantum mechanics an atomic orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. So this question probably come from 526 which give you this.
Okay so lets go back and do this. ORBITAL PICTURE OF BONDING. D There will be fewer electrons ejected.
They student for way to do it. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atoms nucleus. Chemistry questions and answers.
1s 2s 2p x 2p y and 2p zThe two colors show the phase or sign of the wave function in each region. Describe the atomic orbital shown in this picture. This image shows a slice of the 2s orbital that includes the spherical node.
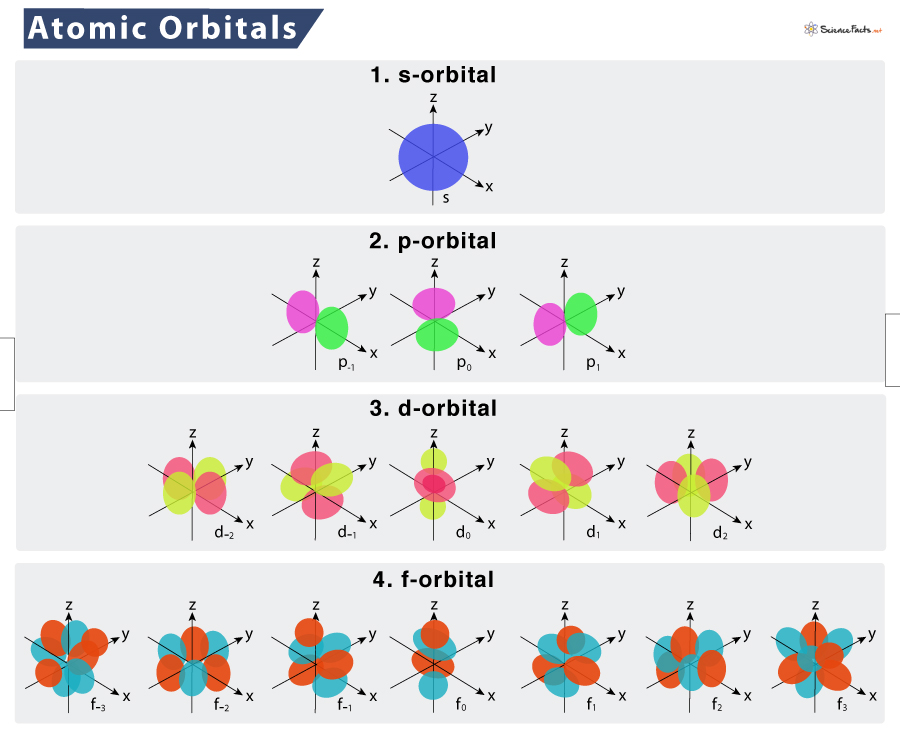
The shapes of the first five atomic orbitals are. The phase of an orbital is a direct consequence of the wave-like properties of electrons. The name of an atomic orbital is usually expressed in terms of a combination of the principal quantum number n and the azimuthal quantum number l.
The color code for the probability is. Z A 2pz B 2py C 2рх y D Зрх X E Зру. Molecular orbital is also created which we simplistically show as a subtraction of the two atomic 1s orbitals σ 1sa - 1sb.
This orbital is called sigma-star σ and is less stable than the two separated atoms. The principle quantum number n. The simple names of the atomic orbitals and the corresponding value of the azimuthal.
There are different types of atomic orbitals. Each picture is domain coloring of a ψx y z function which depend on the coordinates of one electron. Photons are shone on a piece of metal and one electron is ejected for each absorbed photon.
N3 l1 ml0. Describe the atomic orbital shown in bartleby. Describe the atomic orbital shown in this picture.
Describe the atomic orbital shown in this picture. Atomic Orbitals Atomic orbitals are energy states or wave forms of electrons in the atom. The phase of the two interacting orbital or - comes from the sign of orbital wave function and is.
In atomic theory and quantum mechanics an atomic orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. Which of the following sets of quantum numbers could describe an electron in the orbital shown below. A big circle a.
The orange electron density distributions show that the. Z A 2pz B 2py C 2px y D 3px E 3py X. Chemistry questions and answers.
A Ejected electrons will be faster. D 10 four p one since is giving you a in correct order. Of the four well be concerned primarily with s and p orbitals because these are the most common in organic chemistry.
Two atomic orbitals can overlap in two ways depending on their phase relationship. An atomic orbital is a region in space within an atom and around the nucleus where the probability of finding an electron is relatively high. N2 l1 ml-1 c.
Orbitals Chemistry s p d and f Orbital - Atomic Orbitals are of four different kinds denoted s p d and f each with a different shape. Because it is less stable than the two individual atoms it is called an anti-bonding molecular orbital. Molecular orbital theory MO theory provides an explanation of chemical bonding that accounts for the paramagnetism of the oxygen molecule.
Each atomic orbital represents an amount of energy. Z A 2dxy B 3dyz C 3dxy y D 3dx2-y. To see the elongated shape of ψx y z functions that show probability density more directly see pictures of d-orbitals below.
Z y X A 2dxy B 3dyz C 3dxy D 3dx-y. Definition of principle quantum number. The term atomic orbital may also refer to the physical region or space.
This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atoms nucleusThe term atomic orbital may also refer to the physical region or space. Positive Overlapping of Atomic Orbital When the phase of two interacting orbitals is same then the overlap is positive and in this case the bond is formed. There are two basic types of orbitals that can result from such processes.
ORBITAL COMBINATIONS HYBRIDIZATION THEORY MOLECULAR ORBITALS ORBITAL COMBINATIONS Atomic orbitals can be combined and reshaped much like dough to make other orbitals of different shapes and properties. Describe the atomic orbital shown in this picture. What is the value of ℓ for the orbital shown below The orbital shown in this figure has one angular node 1.
It also explains the bonding in a number of other molecules such as violations of the octet rule and more molecules with more complicated bonding beyond the scope of this text that are difficult to describe with Lewis structures. They are for us to three d 10 four p one. The representation of the orbital shown below includes a cutting plane and the probibility of finding an electron in that plane.
Figure 910 Overlap of Two Singly Occupied Hydrogen 1s Atomic Orbitals Produces an HH Bond in H 2. The formation of H 2 from two hydrogen atoms each with a single electron in a 1s orbital occurs as the electrons are shared to form an electron-pair bond as indicated schematically by the gray spheres and black arrows. Um first Im just gonna write down this a r for us too.
Describe the atomic orbital shown in this picture. Atomic Orbitals CAcT HomePage Atomic Orbitals Skills to develop Describe the shapes of ns np and nd atomic orbitals. Show how radial density changes as the radius increases.
The images of atomic orbitals shown above show the isosurface for the orbital. B Ejected electrons will be slower. In graphical representations of orbitals orbital phase is depicted either by a plus or minus sign which have no relationship to electric charge or by shading one lobe.
Names of Atomic Orbitals and the Relationship Between the Different Quantum Numbers that Describe Them. There is nothing wrong about the picture. C There will be more electrons ejected.

Atomic Orbital Fisica Fisica Quantica Fisica E Matematica

Quantum Basis Of Orbitals Chemistry Lessons Organic Chemistry Quantum
0 Response to "Describe the Atomic Orbital Shown in This Picture."
Post a Comment